CURRENT ELECTRICITY :
→Electric Current
→Drift Velocity of electrons and current
→Ohm’s Law
→Current Density
→Resistance, Resistivity, Conductance &
→Conductivity
→Temperature dependence of resistance
→Color Codes for Carbon Resistors
→Series and Parallel combination of
→resistors
→EMF and Potential Difference of a cell
→Internal Resistance of a cell
→Series and Parallel combination of cells
Electric Current:

The electric current is defined as the charge flowing through conductor in one second.
MATHEMATICALLY,current given by
I = q / t
Drift Velocity and Current:
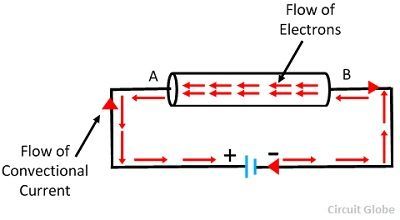
Drift velocity is defined as velocity with which the free electrons get drifted or moved
towards the positive terminal under the effect of the applied electric field.
mathematically,
drift velocity given by,
v d = - (eE / m) τ
current is given as,
I = n e A vd
where,
vd = drift velocity,E =electric field,
e =electronic charge, m =mass of electron, n =number density of electrons, a = acceleration, τ =relaxation time, l= length of the conductor and A =Area of cross-section
Resistance:

The resistance is defined as the opposition offered by the conductor to the flow of electric current through it.
Mathematically,
by ohms law we have,V=IR,
R = V / I
Resistance mathematically given as
I = neA | vd |
I = neA (e |E| / m) τ ( v d = (e|E |/ m) τ)
I =ne2AτV/ml (E=V/L)
V/I=ml/ne2τ A (BY OHM LAWS, R=V/I)
R =ml/ne2τ A
R = m/ne2τ (l/A)
R = ρ (l/A)
where ρ = m/ne2τ ,is resistivity or specific resistance. IT IS PROPERTY OF MATERIAL.
Ohm’s Law:
when physical conditions such as temperature, mechanical
strain, etc. remain constant,
then,electric current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two ends of the conductor .
Mathematically,
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE GIVEN AS,
V=IR
Series combination of resistors:
R = R1 + R2 + R3
R is greatest than all individual resistance, R1, R2, R3,etc CONNECTED IN SERIES
Parallel combination of resistors:
1/R =1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
R is smallest than all individual resistance, R1, R2, R3,etc CONNECTED IN parallel.
emf( electro motive force):
The electro motive force is the maximum potential difference between the two electrodes of the cell when no current is drawn from the cell.
Continue reading with:
- Guass theorem
- Photoelectric effect
- Compton effect
- Semiconductor
- Electrostatics (physics class 12)
- transformer
- Solid state (chemistry class 12)
- Electromagnetic induction
share us:-
emf
|
Potential
Difference
|
emf is the maximum potential
difference
between the two
electrodes
of the cell when no
current
is drawn from the cell
i.e.
when the circuit is open
|
P.D
is the difference of potentials
between
any two points in a closed circuit
|
It is
independent of the
resistance
of the circuit
|
It is
proportional to the resistance
between
the given points or ends.
|
The
term ‘emf’ is used only for
the
source of cells.
|
It is
measured between any two
points
of the circuit
|


I like it 😁😁😁😁
ReplyDeletethank you for your motivation and support.
ReplyDeletenice...jee mains class notes
ReplyDelete